LabUnit M10
With a membrane area of only 336 cm² the Alfa Laval LabUnit M10 is the smallest and most compact of the cross-flow membrane filtration plants offered by Alfa Laval for ultrafiltration and microfiltration. It is a fully integrated system and a popular choice for educational purposes and research and development work
Fully integrated system
The Alfa Laval LabUnit M10 is an extremely versatile, yet easy to use, unit for process development and optimization, scale-up as well as training purposes. The flexibility to install and test two different membranes simultaneously makes it an efficient tool for initial membrane selection.
The Alfa Laval LabUnit M10 can be used with the complete range of flat sheet membranes offered by Alfa Laval for ultrafiltration and microfiltration.
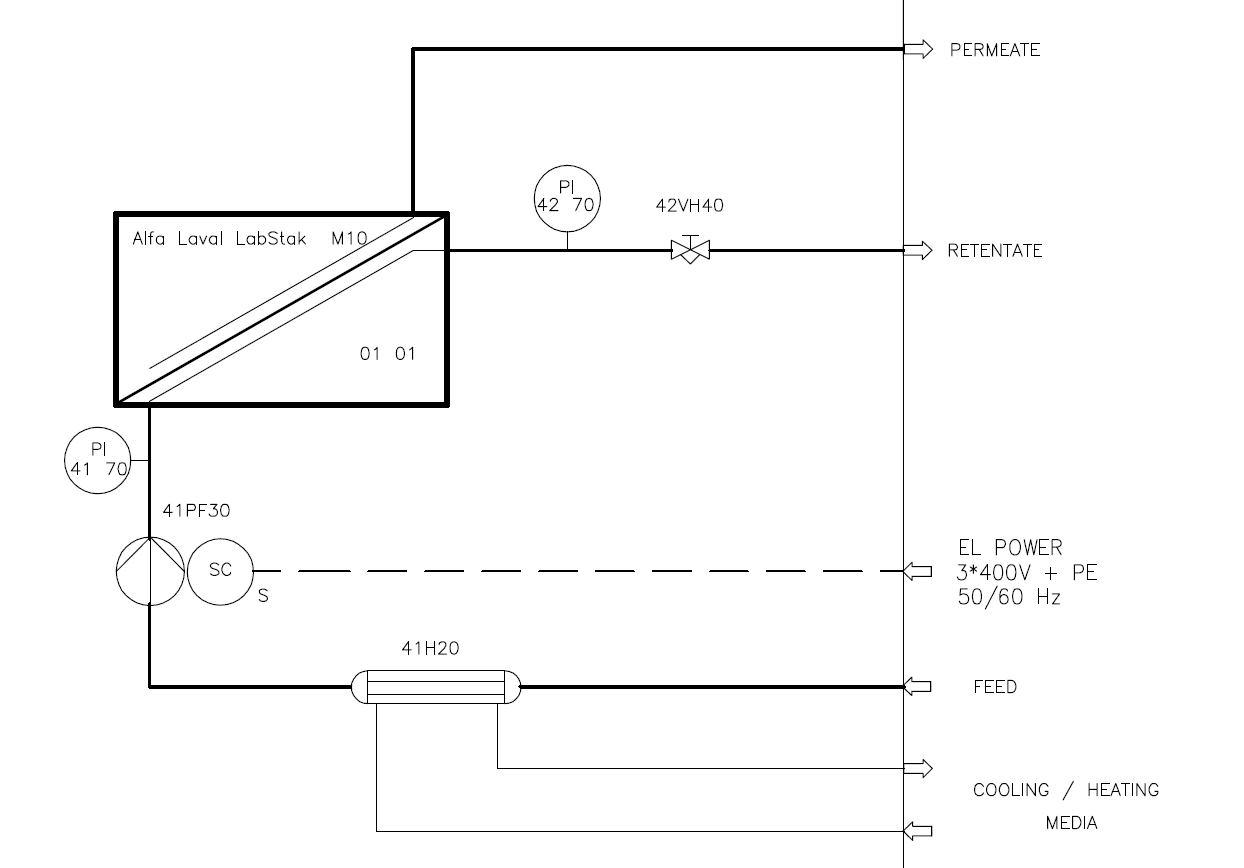
Alfa Laval LabStak® M10
 The Alfa Laval LabStak® M10 unit installed in the Alfa Laval LabUnit M10 is also available as a separate test unit for the same applications as the Alfa Laval LabUnit M10, and with the same distinct properties.
The Alfa Laval LabStak® M10 unit installed in the Alfa Laval LabUnit M10 is also available as a separate test unit for the same applications as the Alfa Laval LabUnit M10, and with the same distinct properties.
Benefits
- fully integrated yet flexible system comprising an Alfa Laval LabStak® M10 complete with necessary pump, pipework, valves, heat exchanger and instrumentation
- easy exchange of membranes
- transparent plate for observation of cross-flow
- simultaneous test of two different membrane types
- high operating temperature (80°C)
- small test media volume
- flow pattern similar to that of larger modules
- all components in compliance with FDA and EEC regulations, allowing use within food and pharmaceutical processing applications
Fonctionnement
Le flux d'alimentation/rétentat s'écoule à travers les canaux ouverts sur la surface de la membrane dans le module à plaques appelé module LabStakTM M10.
La membrane est supportée par des plaques creuses avec de nombreuses fentes qui permettent au perméat d'être collecté et retiré de l'unité via les tubes collecteurs de perméat.
Les modules à plaques utilisent la membrane elle-même, aidés par des bagues de verrouillage ou des bandes, pour sceller l'alimentation/le rétentat et empêcher tout mélange avec le perméat. Cela permet également d'éviter les fuites au niveau de la plaque elle-même.